In Laravel, validation is a crucial aspect of building robust and secure web applications. Laravel provides a powerful and expressive validation system that makes it easy to validate incoming request data. Here's a guide on working with validation in Laravel:
1. Validation in Controllers:
In your controller methods, you can use the validate method to perform validation on incoming requests.
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
public function store(Request $request)
{
$validatedData = $request->validate([
'name' => 'required|string|max:255',
'email' => 'required|email|unique:users',
'password' => 'required|min:8',
]);
// The request data is now validated and available in $validatedData
// Process the form data
}
2. Validation Error Messages:
Laravel automatically redirects the user back to the previous page with validation error messages if validation fails. You can display these messages in your Blade views.
@if ($errors->any())
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<ul>
@foreach ($errors->all() as $error)
<li>{{ $error }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
</div>
@endif
3. Manually Creating Validators:
You can manually create a validator instance if you need more control over the validation process.
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Validator;
$validator = Validator::make($request->all(), [
'name' => 'required|string|max:255',
'email' => 'required|email|unique:users',
'password' => 'required|min:8',
]);
if ($validator->fails()) {
return redirect('form')
->withErrors($validator)
->withInput();
}
// Process the form data
4. Custom Validation Rules:
You can create custom validation rules to suit your application's specific needs.
use Illuminate\Validation\Rule; $validator = Validator::make($request->all(), [ 'status' => [ 'required', Rule::in(['active', 'inactive']), ], ]); // Process the form data
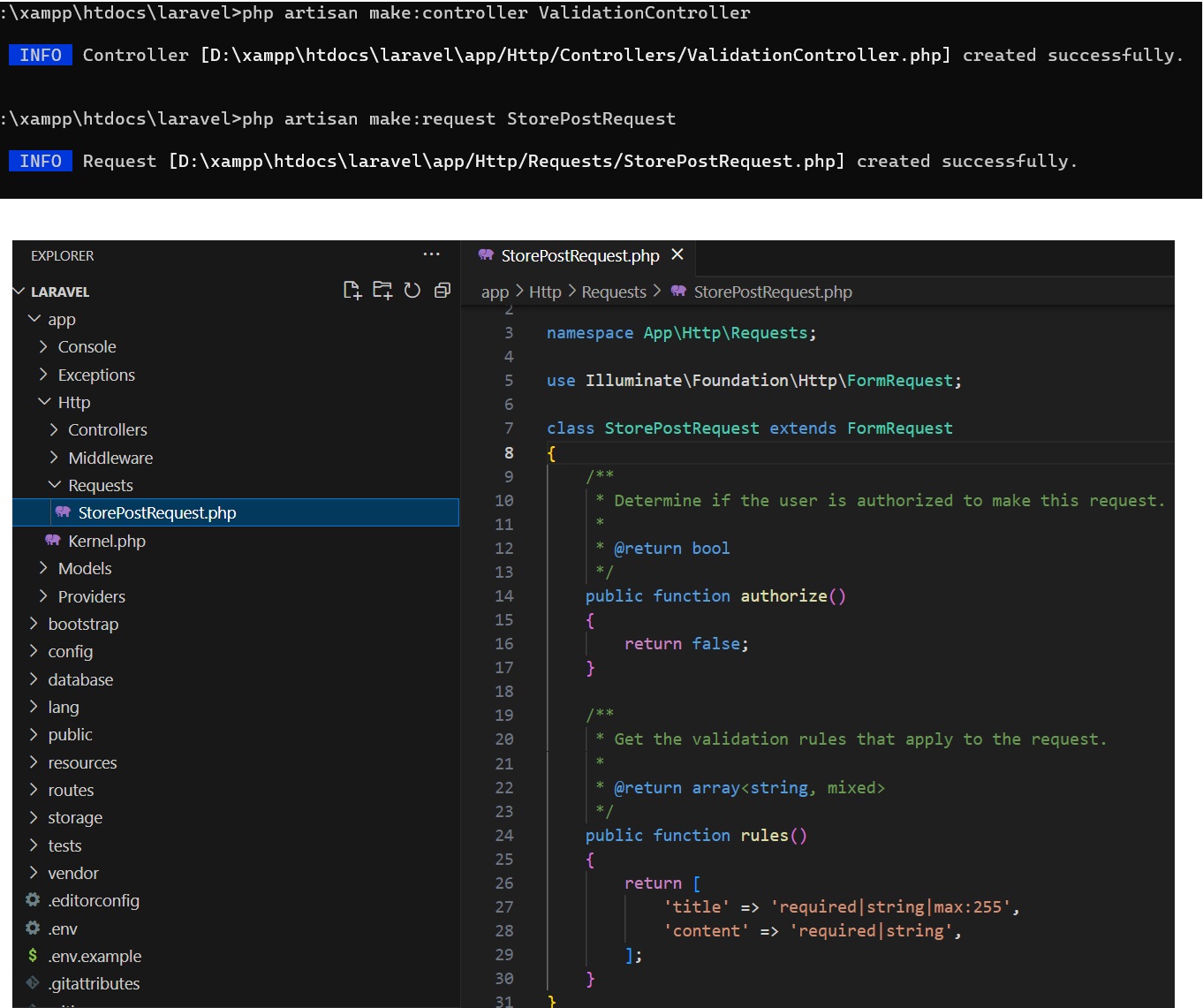
5. Form Request Validation:
You can create form request classes that handle validation. These classes are generated using Artisan.
php artisan make:request StorePostRequest
Then, in your StorePostRequest class:
public function rules()
{
return [
'title' => 'required|string|max:255',
'content' => 'required|string',
];
}
6. Custom Error Messages:
You can customize validation error messages by adding a messages method to your form request or validator.
public function messages()
{
return [
'name.required' => 'The name field is required.',
'email.unique' => 'The email address is already in use.',
];
}
7. Validation with Rule Objects:
You can use rule objects for more complex validation scenarios.
use Illuminate\Validation\Rule;
$validator = Validator::make($request->all(), [
'email' => [
'required',
Rule::unique('users')->ignore($user->id),
],
]);
// Process the form data

Comments